Digital news has become an important part of Americans’ news media diets, with social media playing a crucial role in news consumption. Today, half of U.S. adults get news at least sometimes from social media.

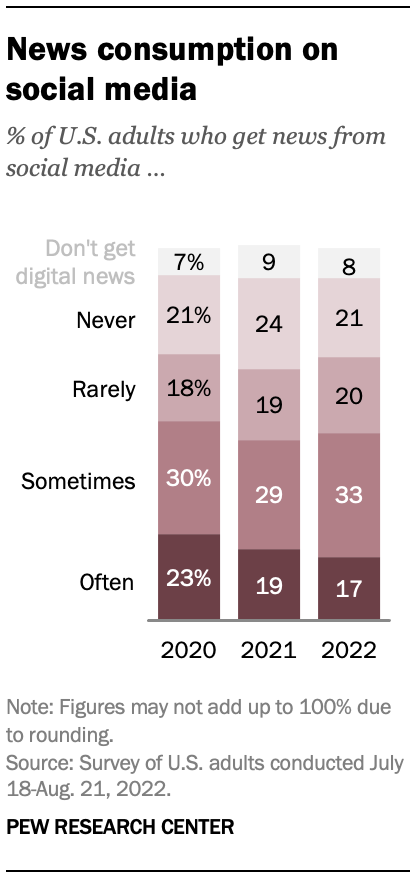
News consumption on social media
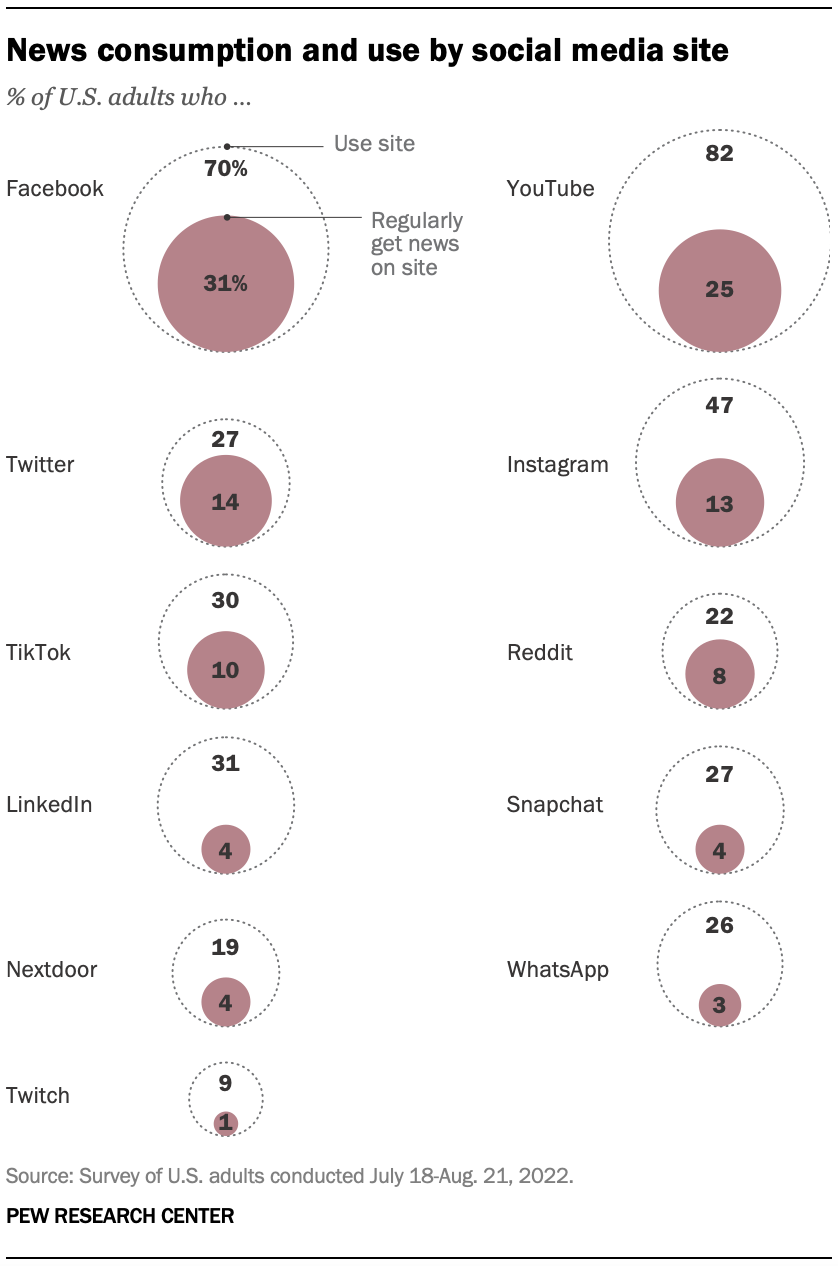
When it comes to where Americans regularly get news on social media, Facebook outpaces all other social media sites. Roughly a third of U.S. adults (31%) say they regularly get news from Facebook.
A quarter of U.S. adults regularly get news from YouTube, while smaller shares get news from Twitter (14%), Instagram (13%), TikTok (10%) or Reddit (8%). Fewer Americans regularly get news from LinkedIn (4%), Snapchat (4%), Nextdoor (4%), WhatsApp (3%) or Twitch (1%).
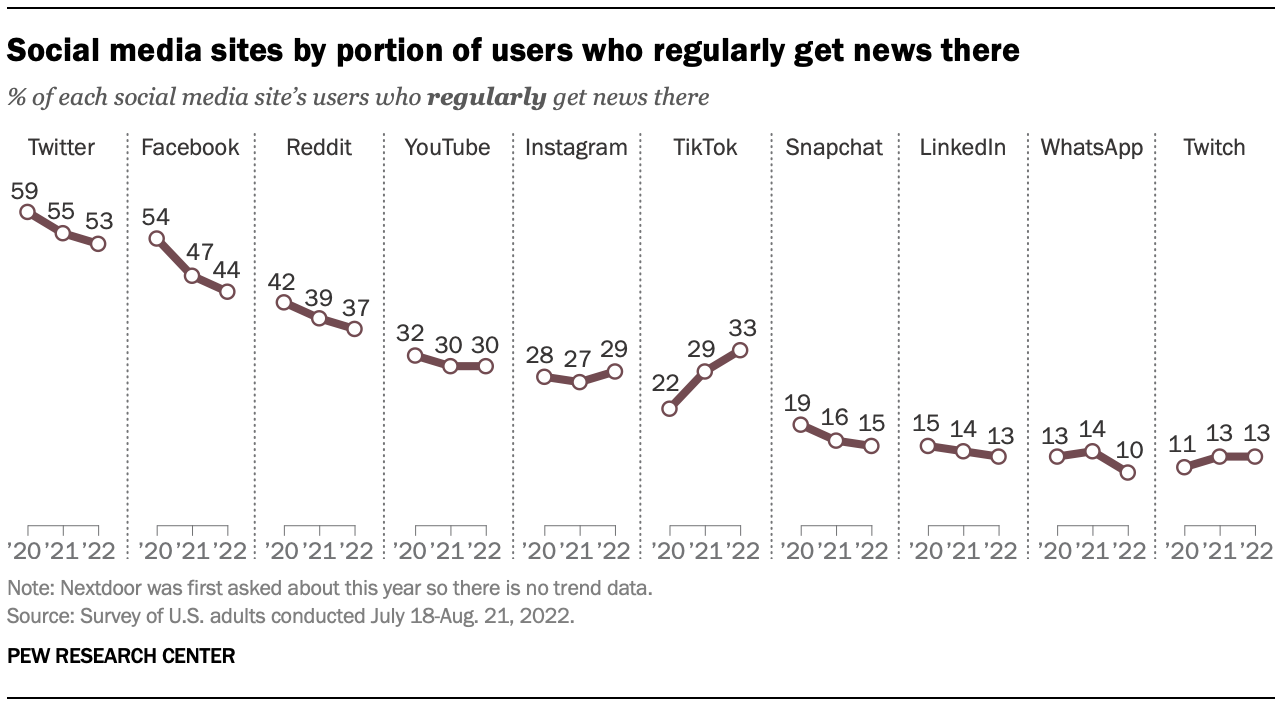
When looking at the proportion of each social media site’s users who regularly get news there, some sites stand out as having a greater portion of users turning to the site for news even if their total audience is relatively small. For example, while Twitter is used by about three-in-ten U.S. adults (27%), about half of its users (53%) turn to the site to regularly get news there. On the other hand, roughly the same share of adults (31%) use LinkedIn, but only 13% of its users regularly get news on the site.

Who consumes news on each social media site
In many cases, there are demographic differences between the people who turn to each social media site regularly for news. On several of the social media sites we asked about, adults under 30 make up the largest share of those who regularly get news on the site. For example, half or more of regular news consumers on Snapchat (67%), TikTok (52%) and Reddit (50%) are ages 18 to 29. Additionally, women make up a greater portion of regular news consumers on Facebook, while the opposite is true for sites like Twitter and Reddit.
Some partisan differences also arise when it comes to who regularly gets news on some social media sites. The majority of regular news consumers on many sites are Democrats or lean Democratic. No social media site included here has regular news consumers who are more likely to be Republicans or lean Republican. (See Appendix for data on U.S. adults in each demographic group who regularly get news from each social media site.)

CORRECTION: (Sept. 23, 2022): The charts in this fact sheet were updated to correct an error in the stated field dates for the data’s underlying survey. The updated text should read: “Source: Survey of U.S. adults conducted July 18 – Aug. 21, 2022.” These changes do not affect the fact sheet’s overall findings.














